Experts meeting at the recent UN Climate Change Conference in Bonn in May have said that a new technology called “Blockchain” could play a major role in tackling climate change.
A Blockchain is a distributed database that is continuously updated and verified by its users. Each added block of data is “chained” and becomes part of a growing list of records, under the surveillance of network members. This technology enables the transfer of assets and the recording of transactions through a secure database.
“As countries, regions, cities and businesses work to rapidly implement the Paris Climate Change Agreement, they need to make use of all innovative and cutting-edge technologies available. Blockchain could contribute to greater stakeholder involvement, transparency and engagement and help bring trust and further innovative solutions in the fight against climate change, leading to enhanced climate actions,” said Alexandre Gellert Paris, Associate Programme Officer at the UNFCCC.
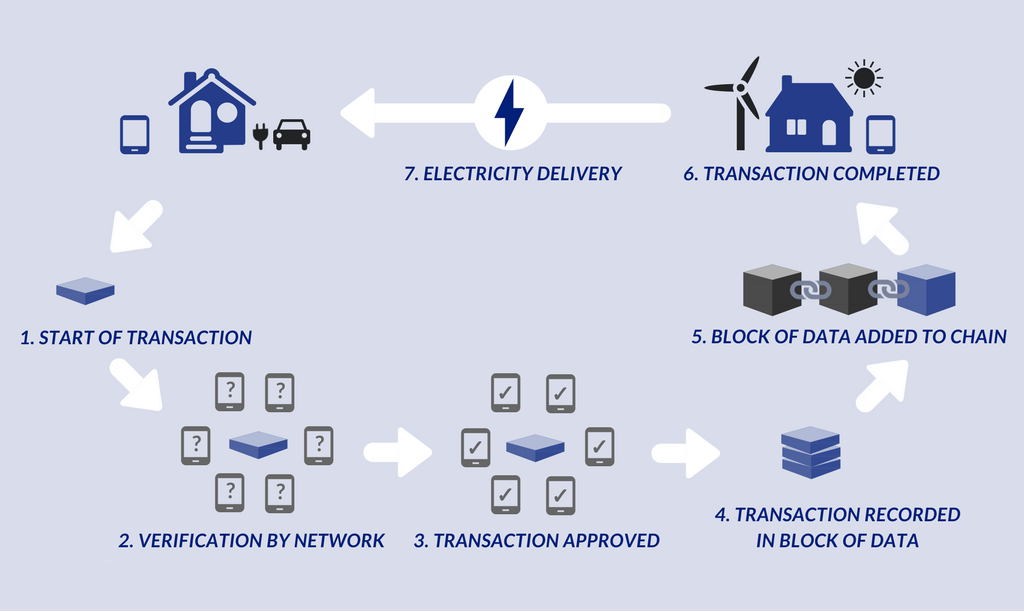
Blockchain technology can be used to develop peer-to-peer trade of clean energy, for certified and facilitated transactions among consumers.
For climate action, Blockchain technology could be used in the following specific ways:
Improved carbon emission trading:
Blockchain could be used to improve the system of carbon asset transactions. For example, IBM and Energy Blockchain Lab are currently working together to develop a Blockchain platform for trading carbon assets in China. Recording carbon assets on a public Blockchain would also guarantee transparency and ensure that transactions are valid and settled automatically.
Facilitated clean energy trading:
The technology could also allow for the development of platforms for peer-to-peer renewable energy trade. Consumers would be able to buy, sell or exchange renewable energy with each other, using tokens or tradable digital assets representing a certain quantity of energy production.
Enhanced climate finance flows:
Blockchain technology could help develop crowdfunding and peer-to-peer financial transactions in support of climate action, while ensuring that financing is allocated to projects in a transparent way.
Better tracking and reporting of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions reduction and avoidance of double counting:
The technology could provide more transparency regarding GHG emissions and make it easier to track and report emission reductions, thereby addressing possible double counting issues. It could serve as a tool to monitor the progress made in implementing the Nationally Determined Contributions, or “NDCs” under the Paris Agreement, as well as in company targets.
Advantages of Blockchain Technology
The first major application of Blockchain technology was the Bitcoin digital currency, launched in 2009, allowing online payments to be transferred directly, without an intermediary. The currency is meanwhile used by millions of people for payments.
Blockchain, the underlying technology operating the Bitcoin should be separated from the currency. It has many other applications in inter-organizational cooperation, including as an efficient way to keep record of transactions and manage data.

Blockchain technology is based on a mutual distributed network, which allows for high-level trust among users and better monitoring over the stored data.
More Work Needed for Blockchain to Fully Support Climate Action
Because of its distributed nature, Blockchain could improve governance and sustainability in support of collective action aimed at tackling climate change. As opposed to centralized or decentralized networks, Blockchain prevents monopolistic control over the system. The technology also records transactions openly and permanently, thus fostering transparency and traceability.
Research on ways to integrate Blockchain into different sectors related to sustainable development is now expanding, and innovation at the intersection of Blockchain and climate change is expected to further develop in the coming years.
Blockchain was also the topic of key sessions during the Innovate4Climate 2017 conference in Barcelona this May, the most important gathering of the private sector on climate change organized by the World Bank Group and others.
The United Nations Climate Change (UNFCCC) secretariat recognizes the general potential of Blockchain technology. In particular, transparency, cost-effectiveness and efficiency advantages, which in turn may lead to greater stakeholder integration and enhanced creation of global public goods are currently viewed as the main potential benefits. The secretariat, therefore, specifically supports initiatives that lead to innovation at the intersection of Blockchain and climate. One of such initiatives is the “Blockchain for Climate” hackathon to be organized by the government of Liechtenstein, Cleantech21, INFRAS and ETH Zürich, in the margin of COP23.
Read more:
A Brief History of Blockchain, by Vinay Gupta for the Harvard Business Review
The environment needs cryptogovernance, by Guillaume Chapron for Nature
The Blockchain and Us, a film by Manuel Stagars
