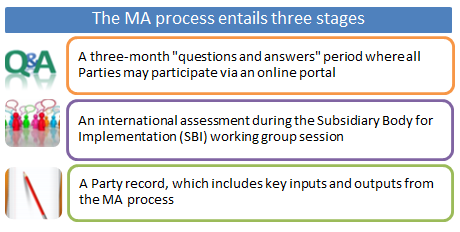
In 2014 the UNFCCC Secretariat launched the multilateral assessment (MA) process as an important part of the global assessment of developed country commitments to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
This page graphically explains how it works and analyses the range of questions asked.
The MA provides an open platform for all 196 Parties under the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) to discuss this progress made by developed countries towards achieving their quantified economy-wide emission reduction targets.
It is a central part of the newly established international assessment and review (IAR) process for developed country Parties under the UNFCCC.
The first multilateral assessment under the first IAR cycle for 17 developed country Parties was conducted at the Conference of the Parties (COP 20) in Lima, Peru in December 2014.
The Second Working Group Session of the multilateral assessment (MA) process was held in Bonn on 4–5 June 2015, with 24 Annex I Parties being assessed of their quantified economy-wide emission reduction targets, as well as their progress towards achieving these targets.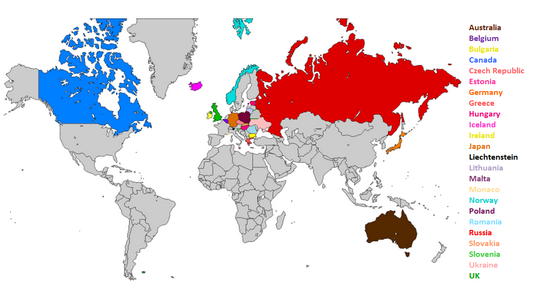
The interaction amongst Parties was constructive and positive. Parties highlighted the importance of the MA process in improving transparency and building trust amongst Parties.
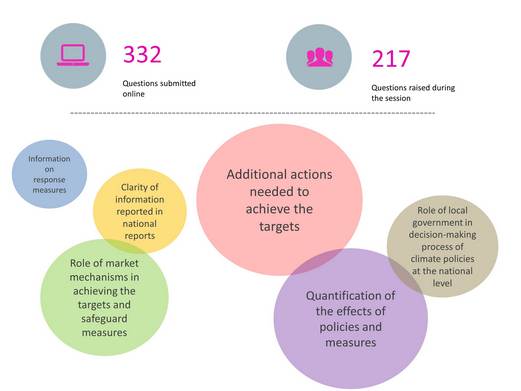
Altogether 217 questions were raised for the 24 Parties during the 2-day MA session. This is in addition to the 332 written questions that were received online prior to the MA session.
Most of the questions focused on mitigation actions by Parties across various sectors, quantification of the effects of policies and measures, the role of market mechanisms in fulfilling the 2020 targets, safeguard measures in place to avoid double counting of credits, and the role of local/ regional governments in the decision-making process of climate polices at the national level. There were also a number of questions that sought clarification on policies and measure in reducing emissions from international shipping and the lack of information in the biennial reports on response measures.
During the session, Parties shared success stories and best practices in policy instruments and innovations, such as the use of market-based approach in promoting renewables and improving energy efficiency.
Overall, this multilateral assessment process provided a wealth of information that enhanced the Parties ‘understanding of climate actions in other countries.
What’s next
With this MA session, the first round of the International Assessment and Review Process (IAR) process for most Annex I Parties is completed, with the exception of Belarus and Kazakhstan, which will be multilaterally assessed in Paris later this year.
The Party records, webcasts of and presentations by the assessed Parties during the MA session can be found on their respective Party page